

Like an atomic orbital, a molecular orbital is full when it contains two electrons with opposite spin. The region of space in which a valence electron in a molecule is likely to be found is called a molecular orbital ( Ψ 2). Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). According to the molecular orbital theory, molecular orbitals of a molecule is formed by. Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in molecules are limited to discrete (quantized) energies. The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. This diagram is based upon the molecular orbital theory. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom. As atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals. Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. MO Diagram - A molecular orbital diagram, also known as a MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool used to explain chemical bonding in molecules using molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. Needs multiple structures to describe resonance We again fill the orbitals according to Hund’s rules. To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for O 2, we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure 9.10.1.
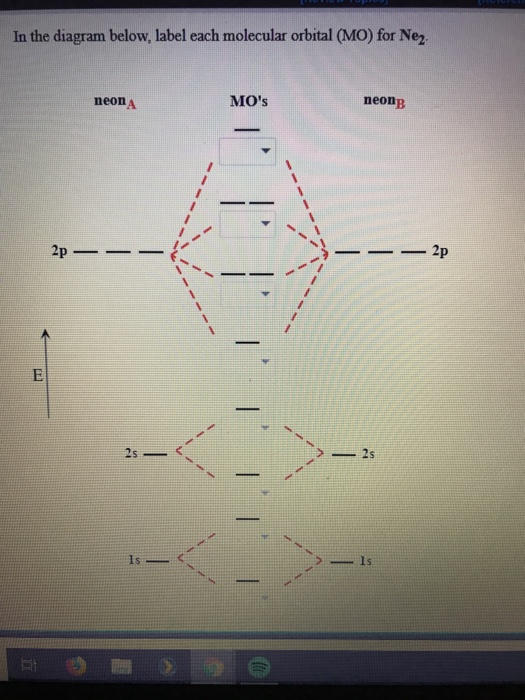
This diagram shows 8 electrons in bonding orbitals and 6 in antibonding orbitals, resulting in a bond order of 1. The bond length in the oxygen species can be explained by the positions of the electrons in molecular orbital theory. (a) For F 2, with 14 valence electrons (7 from each F atom), all of the energy levels except the highest, 2 p z are filled. Predicts the arrangement of electrons in molecules 1: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules. OF has 14 valence electrons, four in the 2p orbitals (see the diagram in the answer to Problem 5.9). Predicts molecular shape based on the number of regions of electron density The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the infinite-fold rotation axis of the orbitals on the basis of the change in wave function sign upon crossing the nodes on the bond axis. \): Comparison of Bonding Theories Valence Bond TheoryĬonsiders bonds as localized between one pair of atomsĬonsiders electrons delocalized throughout the entire moleculeĬreates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d…) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp 2, sp 3…)Ĭombines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*)Ĭreates bonding and antibonding interactions based on which orbitals are filled


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
